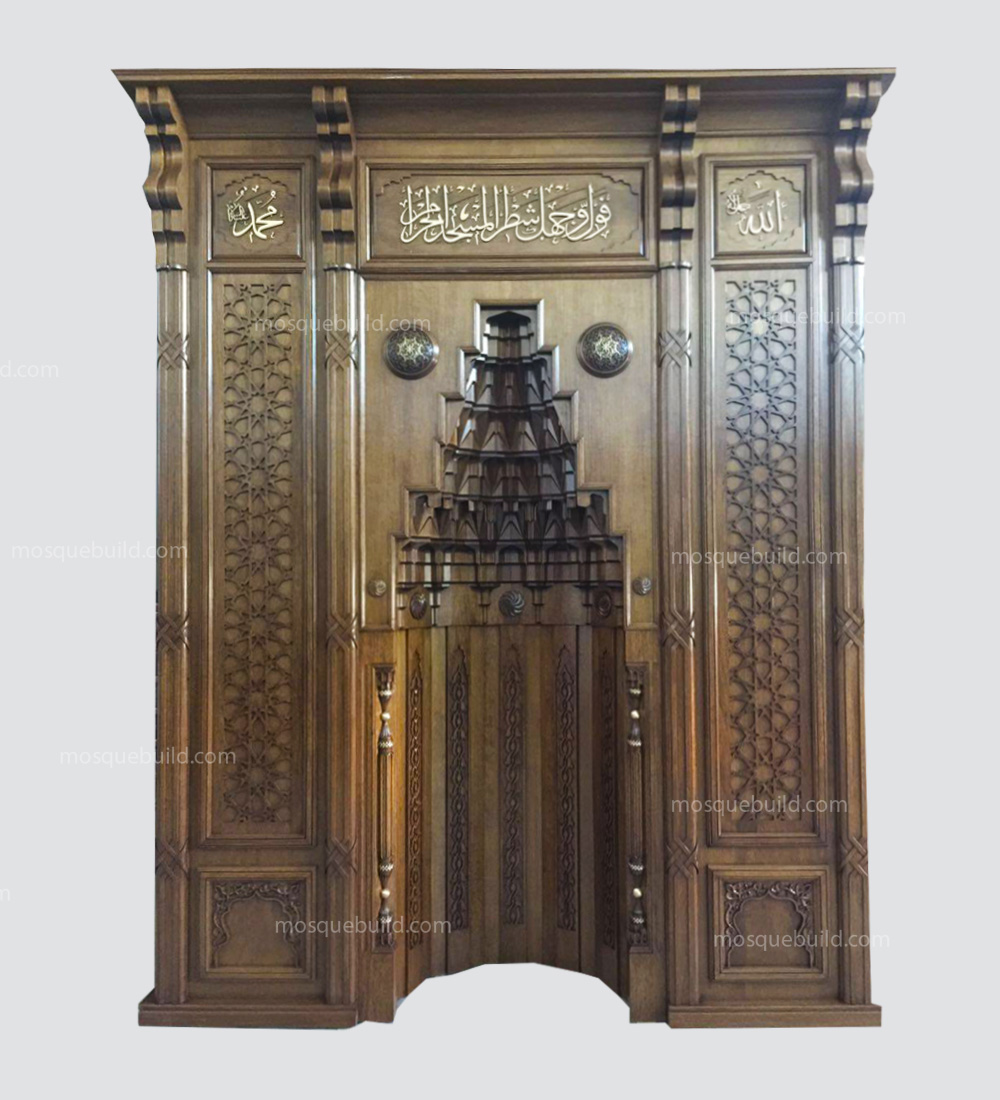
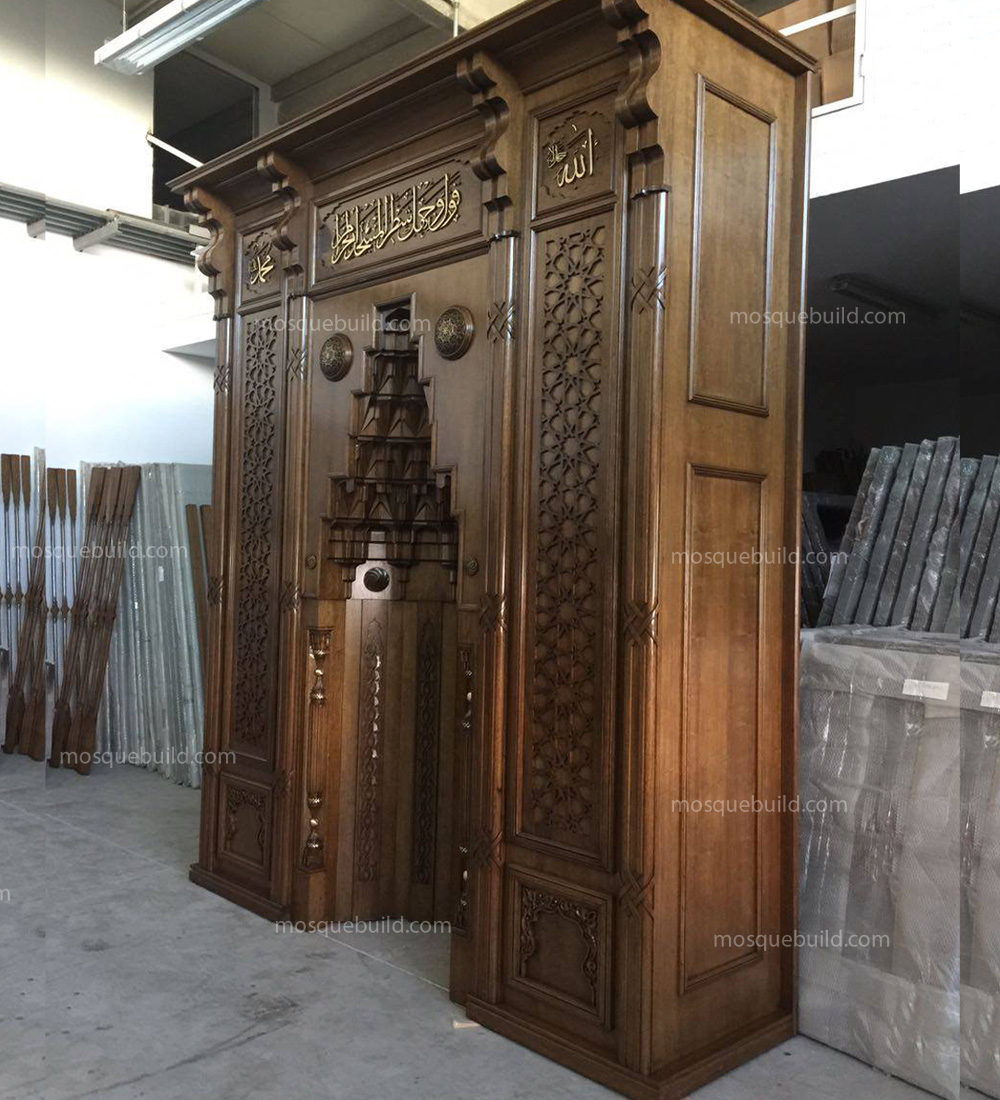
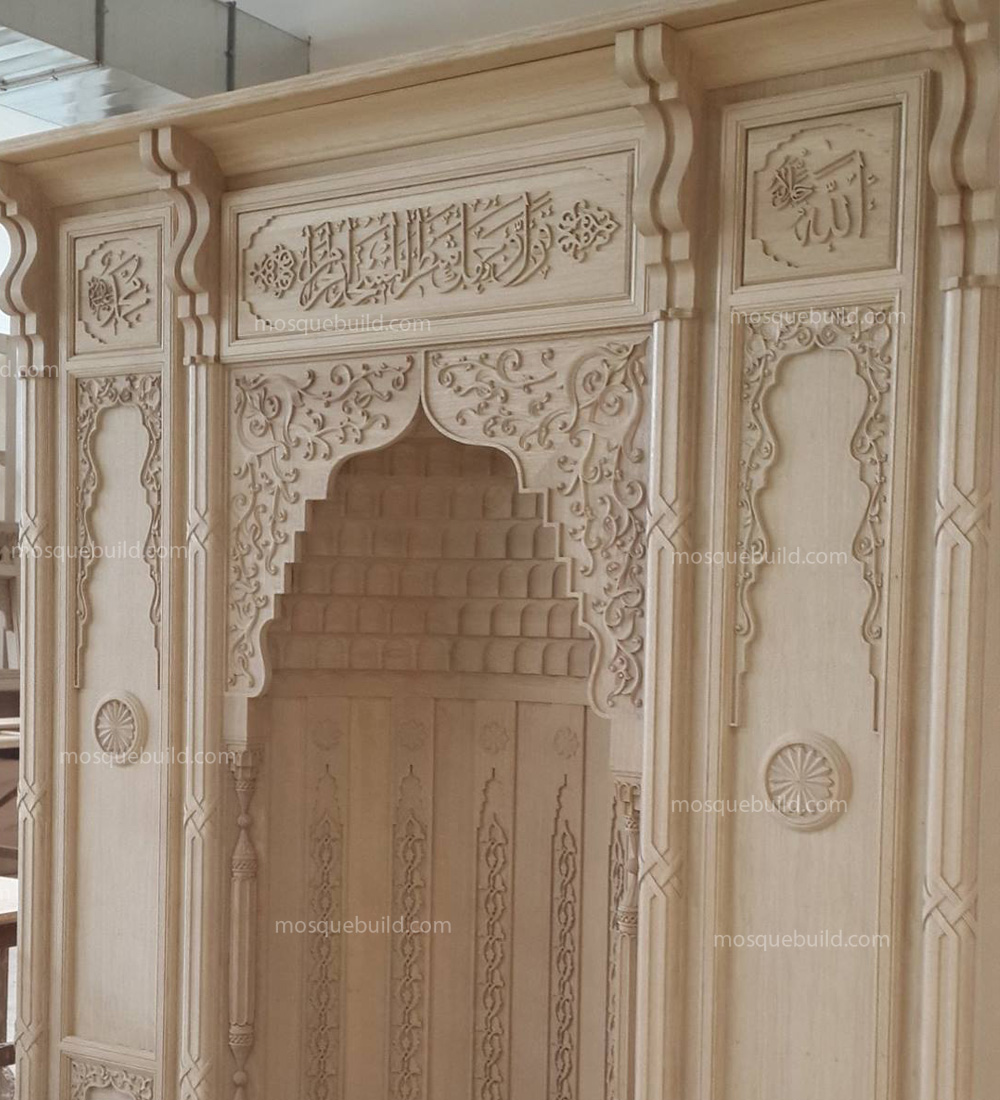
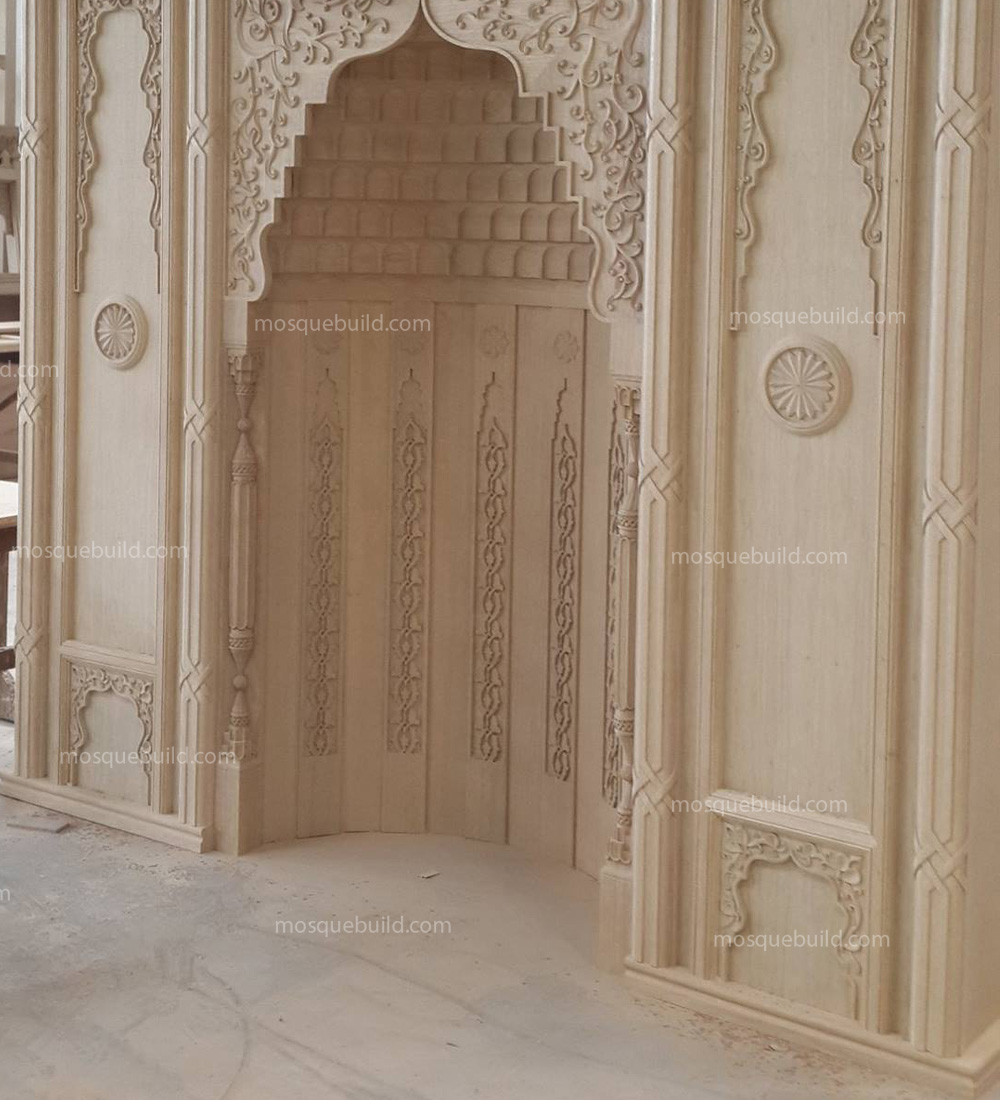
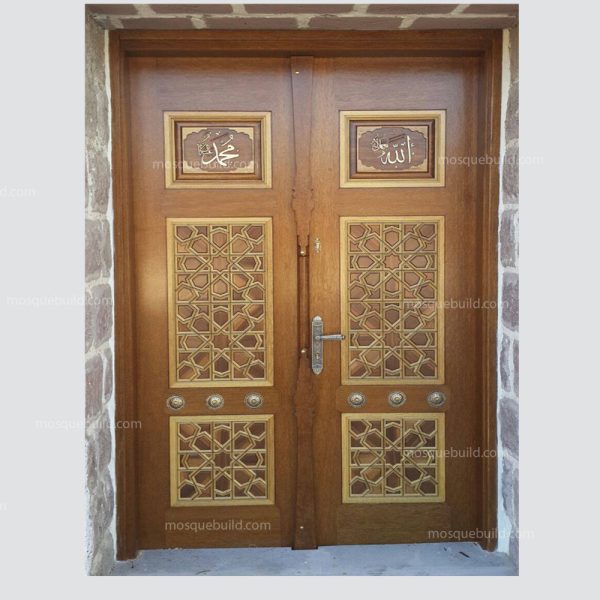
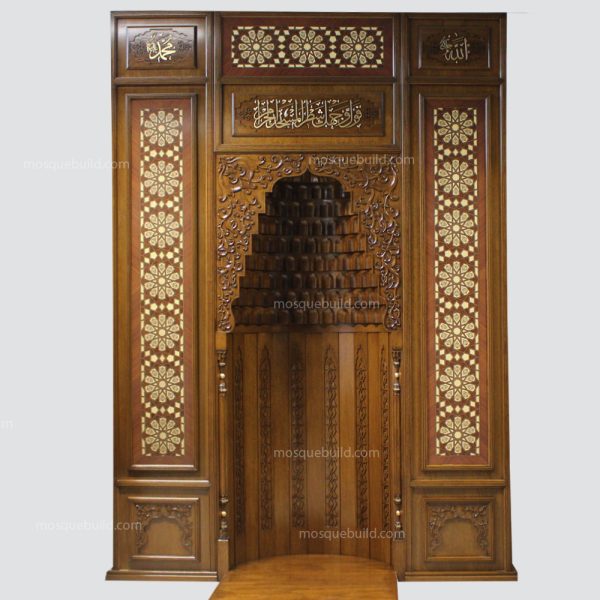
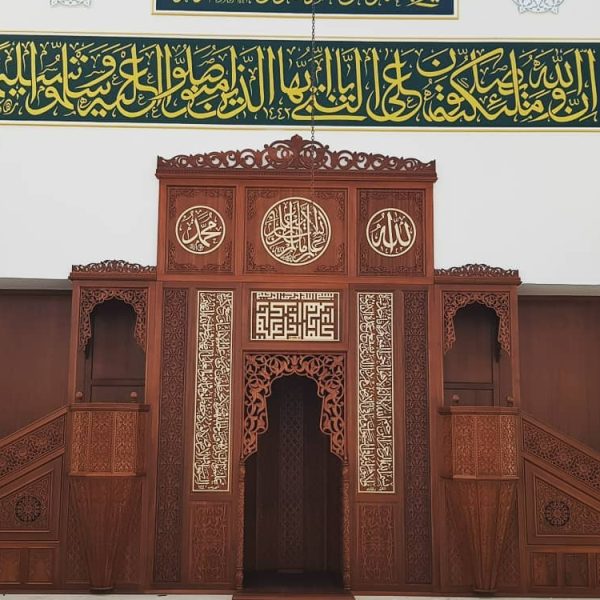
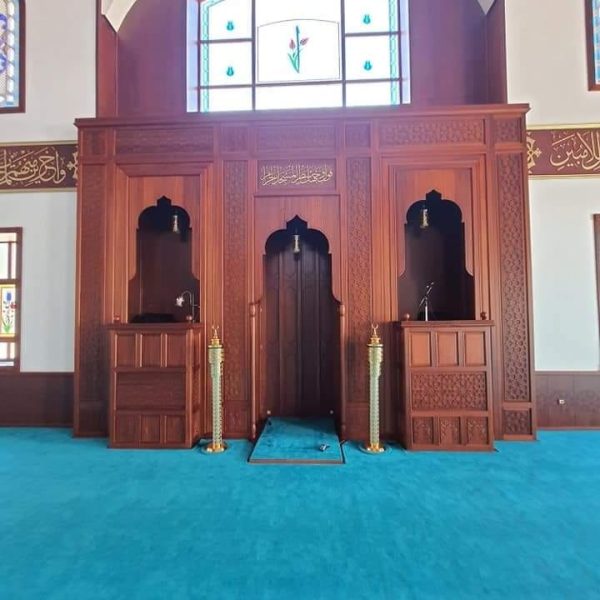
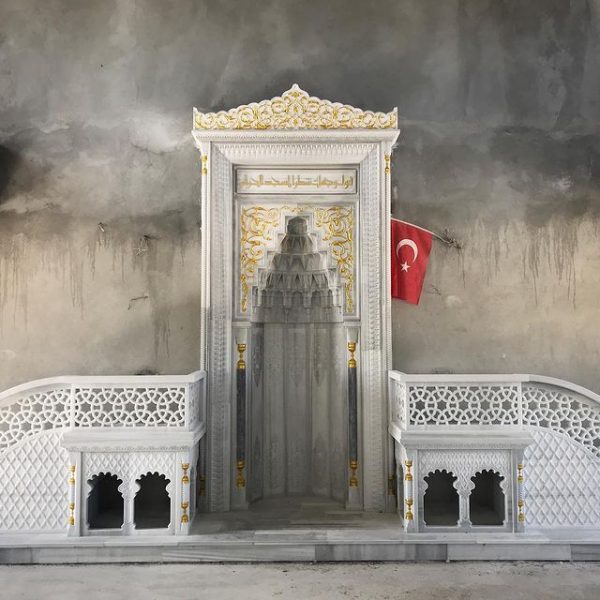
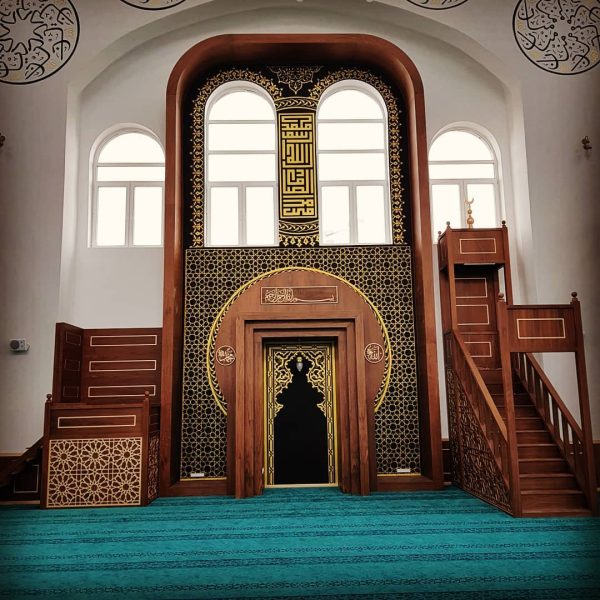
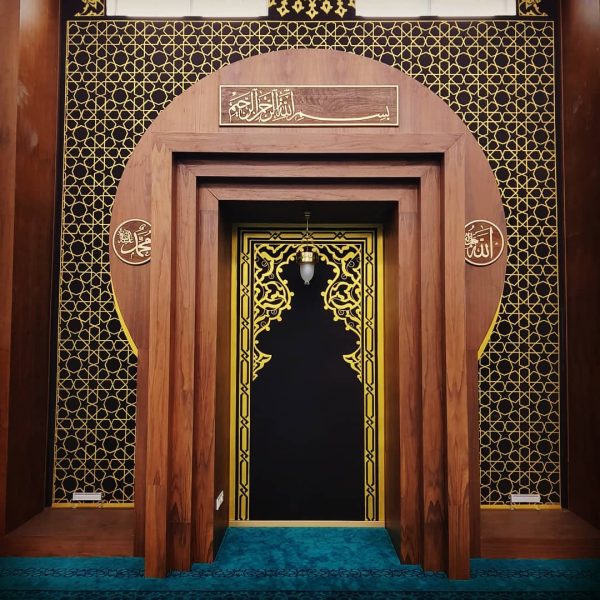
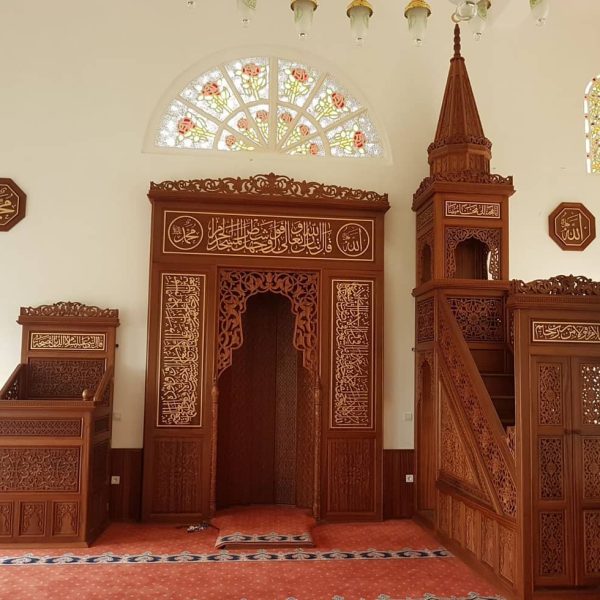
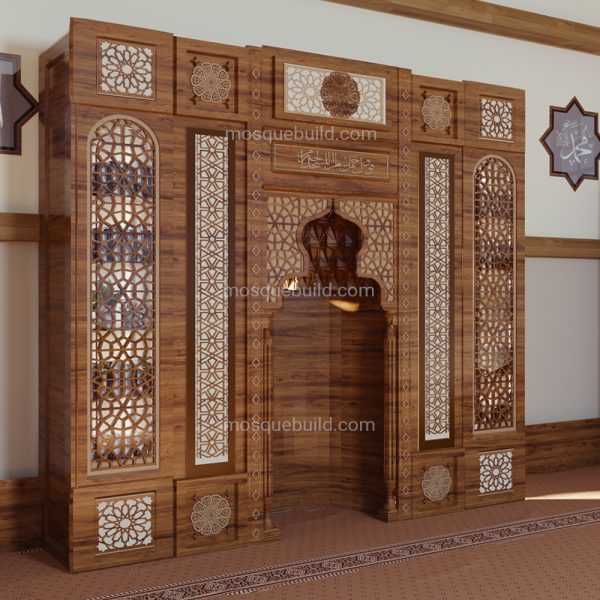
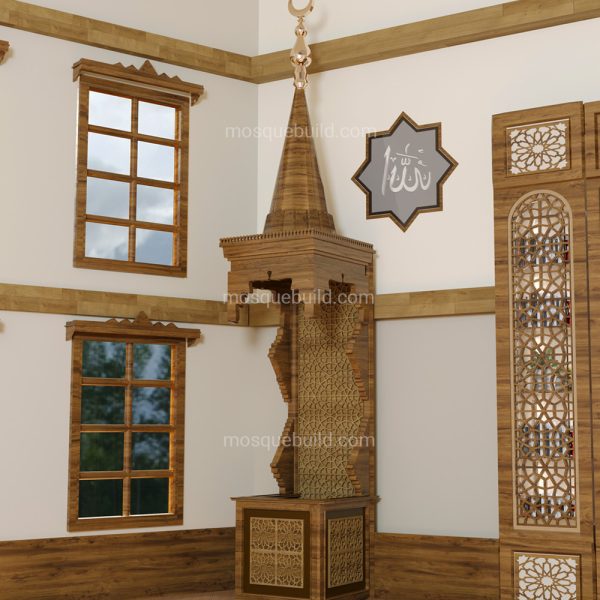
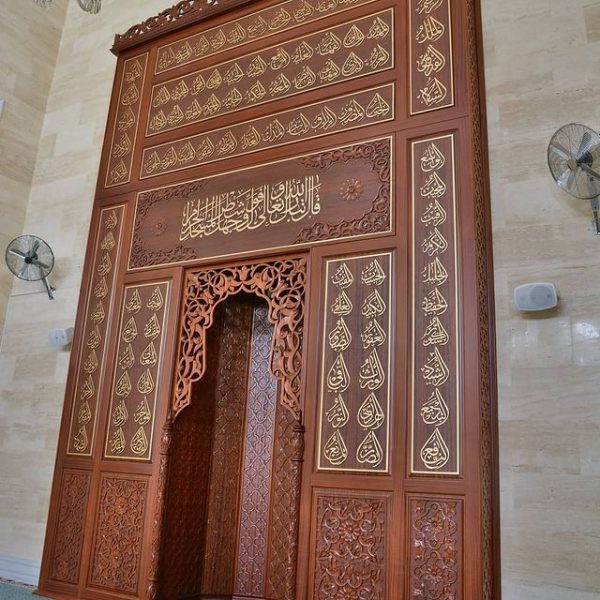
Mihrab is one of the most important elements of Islamic architecture. The mihrab, which shows the qibla direction of the mosques and determines the place where the imam-hatib will pray, is also a symbolic representation of the Islamic faith.
The classical mihrab is a type of mihrab that emerged in the Ottoman Empire in the 16th century and was widely used until the 19th century. The most distinctive feature of the classical mihrab is that it consists of a niche decorated with muqarnas, ending with a pointed arch. The pointed arch of the mihrab niche represents the symbolic ascent of the Islamic faith into the sky. Muqarnas are a traditional ornamental motif of Islamic art.
The development of the classical mihrab can be seen in the works of Mimar Sinan in the 16th century. Sinan determined the basic features of the classical mihrab by skillfully using pointed arches and muqarnas in the mihrabs. After Sinan’s works, the classical mihrab began to be widely used in the Ottoman Empire.
The classical mihrab was built in mosques throughout the Ottoman Empire until the 19th century. During this period, the classical mihrab was interpreted in different ways in different regions. For example, while the classical mihrabs in Egypt are decorated with colorful stones, the classical mihrabs in Iran have more spectacular and complex decorations.
The classical mihrab was also used in mosques built in the 20th century. However, with the influence of modern architecture in the 20th century, the use of classical mihrabs decreased. However, the classical mihrab is still used in many mosques today.
The history of the classical mihrab reflects the development of Islamic architecture and the symbolism of the Islamic faith. The classical mihrab is one of the most important and beautiful examples of Islamic architecture.
Classical Mihrab Types
Classical altars can be divided into different types according to their basic features. Some of these types are:
Pointed arched mihrab: The most common type of classical altar. It consists of a niche decorated with muqarnas, ending with a pointed arch.
Arched mihrab: It is a type of mihrab in which a round arch is used instead of a pointed arch.
Round mihrab: It is a type of niche-shaped mihrab that does not use arches.
Classic Altar Decorations
Classical altars are usually decorated with rich decorations. These decorations consist of geometric motifs, floral motifs, human and animal figures.
Geometry motifs are the most commonly used motifs in classical altar decorations. These motifs have an important place in Islamic art and represent order, harmony and perfection.
Floral motifs are another important motif used in classical altar decorations. These motifs represent the beauty and vitality of nature in Islamic art.
Human and animal figures are less commonly used in classical altar decorations. These figures usually represent some religious figures that have an important place in Islamic art.
The Importance of the Classical Mihrab
The classical mihrab is one of the most important and beautiful examples of Islamic architecture. The classical mihrab is a symbolic representation of the Islamic faith and reflects the development of Islamic architecture.